Table of Content
- Industry Standard Architecture (ISA)
- Extended Industry Standard Architecture (EISA)
- Micro Channel Architecture (MCA)
- VESA Local Bus (VESA)
- Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI)
- PCI-X
- Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP)
- PCI Express (PCI-E, PCIe)
- Intelligent Input/Output (I2O)
- InfiniBand Architecture (IBA)
Industry Standard Architecture (ISA)
- Introduced in 1984 with the IBM PC AT
- 8- or 16-bit bus
- 98-pin connector
- 8 MB/sec bandwidth

Extended Industry Standard Architecture (EISA)
- Introducted in 1987 to compete against MCA bus
- 32-bit bus
- Dual purpose bus
- Replace by better performing PCI bus
Micro Channel Architecture (MCA)
- Developed by IBM in 1987
- Not widely adopted by vendors as IBM charged royalties for the rights to use it
- 116-pin connector
- Made extinct by the license-free EISA bus and later by the PCI bus
VESA Local Bus (VESA)
- Developed in 1992 as an extension of video memory
- 116-pin connector
- Replaced by better performing AGP bus
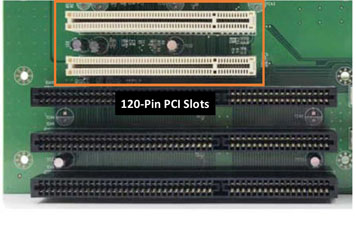
Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI)
- Standard bus on almost all computers of the era
- Developed with open standards (no licensing fee to use)
- Hot-swappable
- Plug-and-play compatible
- 32-bit bus
- Can support 5 devices at a time
PCI-X
- 64-bit wide bus
Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP)
- Introduced by Intel in 1997
- Used mostly with AGP-compatible video cards
- Original AGP standard (AGP 1x) offered data transfer rate of 264MB/sec
- 32-bit wide bus
- 132-pin connector
- AGP 2x, 4x, and 8x offered data transfer rate of 528MB/sec, 1GB/sec,and 2GB/sec respectively
- Replaced by PCI Express in late 2000s
PCI Express (PCI-E, PCIe)
- Developed by Intel in 2004
- Formerly known as 3GIO
- 1-bit wide bus (serial communication)
- Bandwidths:
- PCI-E 1x: 250 MB/sec
- PCI-E 2x: 500 MB/sec
- PCI-E 4x: 1000 MB/sec
- PCI-E 8x: 2000 MB/sec
- PCI-E 16x: 4000 MB/sec
- PCI-E 32x: 8000 MB/sec
Intelligent Input/Output (I2O)
- Designed in 1996 by Intel and I20
- Works along with a PCI bus
- Uses special input and output drivers to "think for itself" thus freeing up computer resources
- End of life in October 2000
InfiniBand Architecture (IBA)
- Conceived in 1999
- High-speed / high-output bus to replace PCI
- Low latency


