Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation headquartered in Santa Clara, California and has been in the semiconductor manufacturing business for decades. Since launching their first processor (also referred to as a central processing unit, or CPU for short) in 1971, Intel (which stands for "INTegrated ELectronics") has since made significant technological advances in chip design throughout the years to bring new generations of processors to the masses.
While competitors have come and gone over the decades, Intel stood as the leader in the processor market. With each generation, processors became more powerful and faster. By the early 21st century, Intel's processors were found in more than 80% of the computers worldwide. While it is known for their microprocessors, Intel also manufacturers wireless products, storage and memory devices, networking equipment, and more. The illustrated timeline below summarizes the major families of microprocessors Intel has produced since launching their first 4004 CPU in 1971.
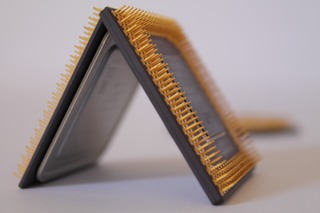
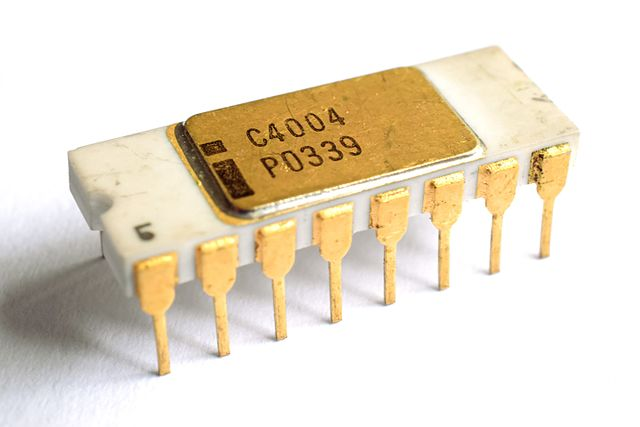
Intel 4004 Processor
November 15, 1971Intel's first processor, this 4-bit design was used in Nippon Calculating Machine Corporation Busicom 141-PF printing calculator.
- Clock Speed: 740KHz
- Type: 4-bit, Single-Core
- Transistors: 2,300
- Manufacturing Technology: 10 micron

Swtpc6800 Michael Holley, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
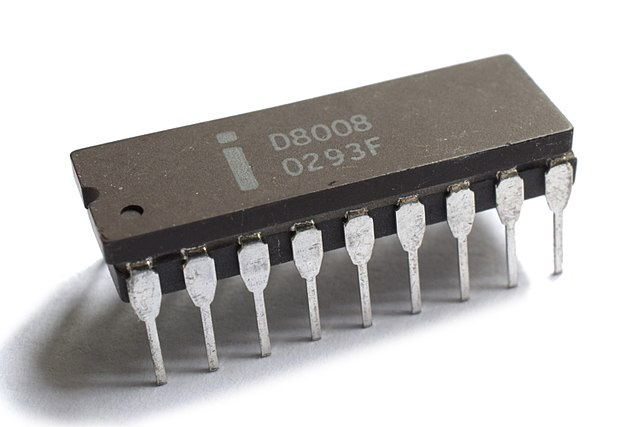
Intel 8008 Processor
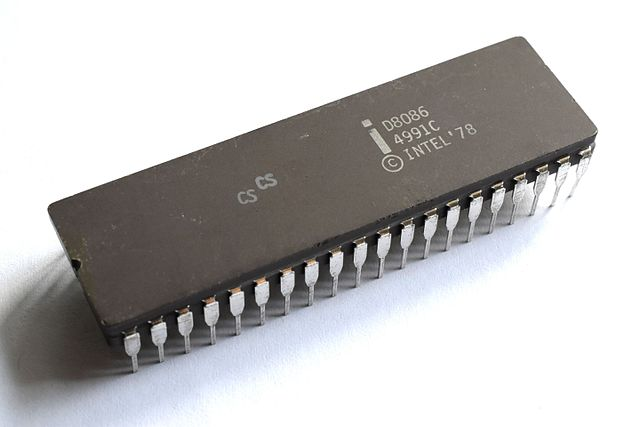
April 1972Intel 8086 Processor
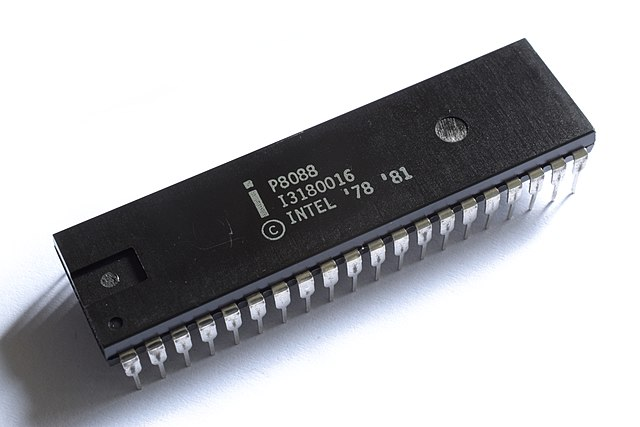
June 8, 1978Intel 8088 Processor
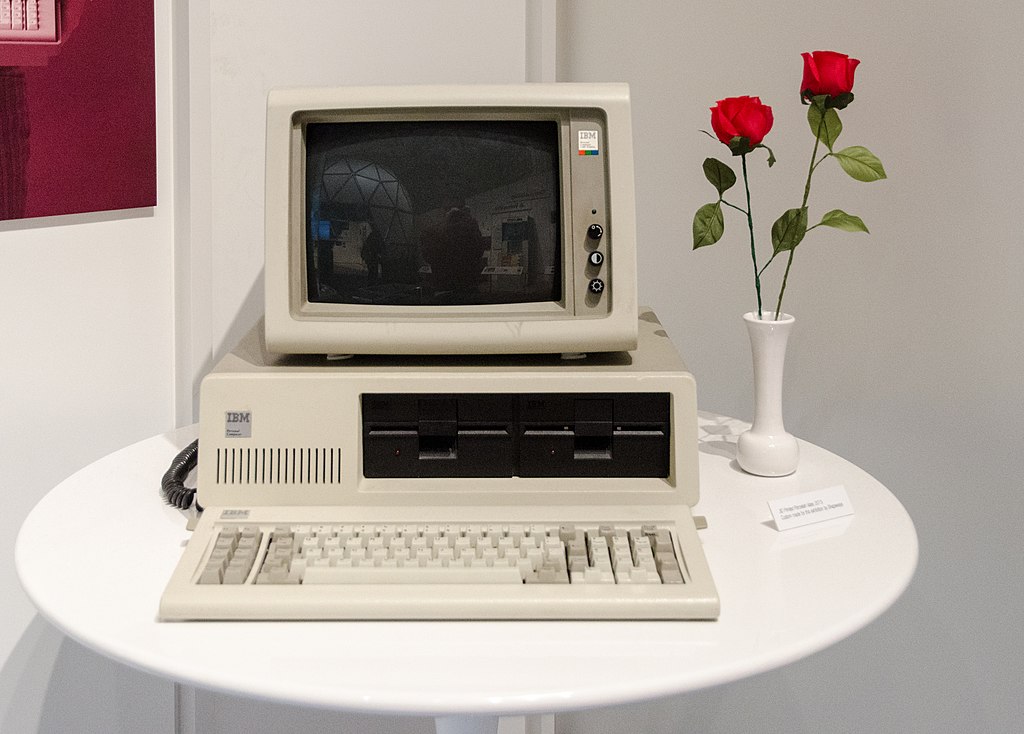
June 1979Powering the IBM 5150 (aka IBM Personal Computer or IBM PC) and clones, this processor was identical to the 8086 with the exception of its 8-bit external data bus width.
- Clock Speed: 5-16MHz
- Type: 16-bit, Single-Core
- Transistors: 29,000
- Manufacturing Technology: 3 micron


edwardhblake, CC BY 2.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Intel 80386DX Processor
October 17, 1982Intel's first 32-bit processor that has a 32-bit external bus and a 32-bit address bus. In the i386 processor family, the 'DX' stood for 'Double word eXternal' referring to the 32-bit external bus.
- Clock Speed: 16-33MHz
- Type: 32-bit, Single-Core
- Transistors: 275,000
- Manufacturing Technology: 1.5 micron
Intel 80386SX Processor
June 16, 1988Lower cost variant of the 80386DX that has a 16-bit external bus and a 24-bit address bus. In the i386 processor family, the 'SX' stood for 'Single word eXternal' referring to the 16-bit external bus.
- Clock Speed: 16-33MHz
- Type: 32-bit, Single-Core
- Transistors: 275,000
- Manufacturing Technology: 1.5 micron
Intel 80386SL Processor
October 15, 1990Designed for laptops, this a low-power variant of the 80386DX processor with built-in power management feature.
- Clock Speed: 20-25MHz
- Type: 32-bit, Single-Core
- Transistors: 855,000
- Manufacturing Technology: 1 micron
Intel 80486SX Processor
April 22, 1991Lower cost variant of the 80486DX that has the internal floating point unit (FPU) (aka math coprocessor) disabled. In the i486 processor family, the 'SX' refers to a 486 processor without an integrated math coprocessor.
- Initial Clock Speed: 20MHz
- Type: 32-bit, Single-Core
- Transistors: 1.2 Million
- Manufacturing Technology: 1 micron
Intel 80486DX2 Processor
March 3, 1992- Initial Clock Speed: 50MHz
- Type: 32-bit, Single-Core
- Transistors: 1.2 Million
- Manufacturing Technology: 0.8 micron
Intel 80486SL Processor
November 9, 1992Designed for laptops, this was a low-power variant of the 80486DX processor.
- Initial Clock Speed: 20MHz
- Type: 32-bit, Single-Core
- Transistors: 1.4 Million
- Manufacturing Technology: 0.8 micron
Intel Pentium Pro Processor
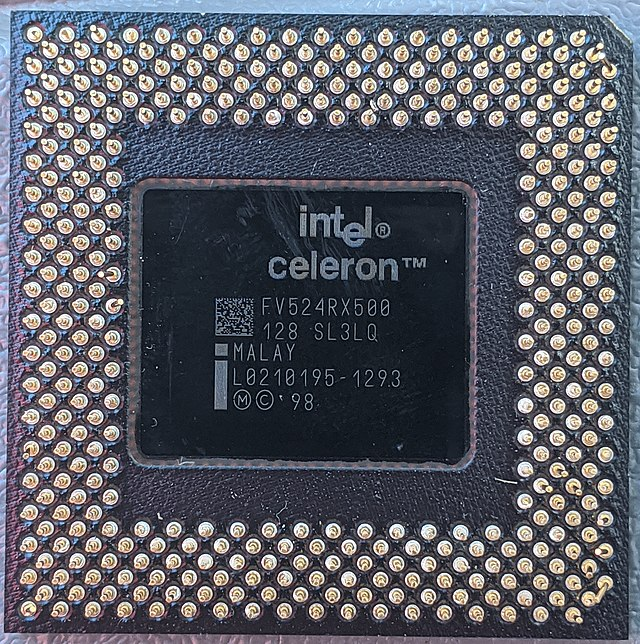
November 1, 1995Intel Celeron Processor
1998Aimed at lower cost computers, this was Intel's response to competitors such as AMD and Cyrix to regain shares in the low-end budget computer market.
- Initial Clock Speed: 266MHz
- Type: 32-bit, Single-Core
- Transistors: 7.5 Million
- Manufacturing Technology: 0.25 micron
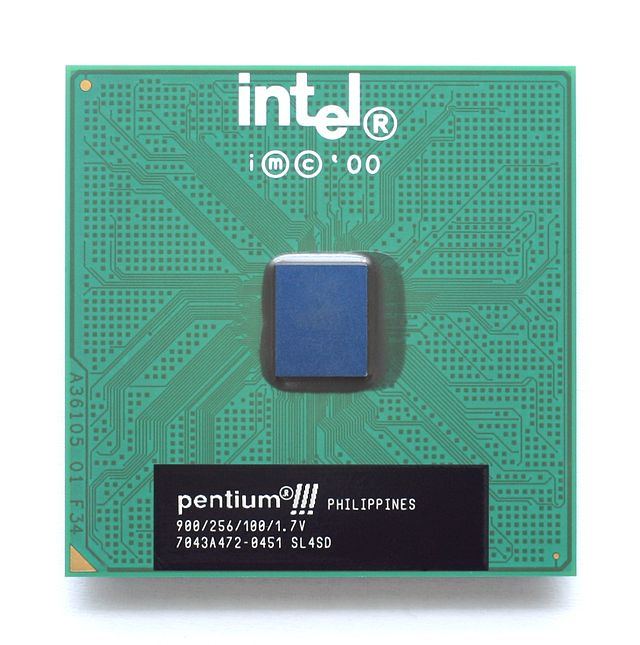
Intel Pentium III Processor
February 26, 1999The Intel Pentium III family consists of a few sub-families targeting different segments of computer market:
- Pentium III Xeon - high performance version targeted towards servers and business workstations.
- Pentium III desktop processors - targeted towards home and business desktop computers.
- Desktop Celeron - low-cost version targeted towards budget and light-use computers.
- Mobile Pentium III and Pentium III-M - mobile versions of the Pentium III processor intended for laptops.
- Mobile Celeron - mobile version of Intel Celeron processor targeted towards budget laptops.
- Clock Speeds: 400 to 1,400MHz
- Type: 32-bit, Single-Core
- Transistors: 9.5 Million
- Manufacturing Technology: 0.25 micron
Intel Atom Processor
April 2008The Intel Atom line are low-power consuming, low-cost, and low-performance processors designed for netbooks, IoT devices, or other devices or systems that are function-specific.
- Initial Clock Speed: 1.86GHz
- Type: 32-bit, 1 to 8-Core
- Transistors: 47 Million
- Manufacturing Technology: 45 nm
Intel Core i7 Processor
November 17, 2008- Clock Speeds: 2.66 - 3.2GHz
- Type: 64-bit, 4 to 10-Core
- Transistors: 731 Million
- Manufacturing Technology: 45 nm

Eric Gaba, Wikimedia Commons user Sting, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
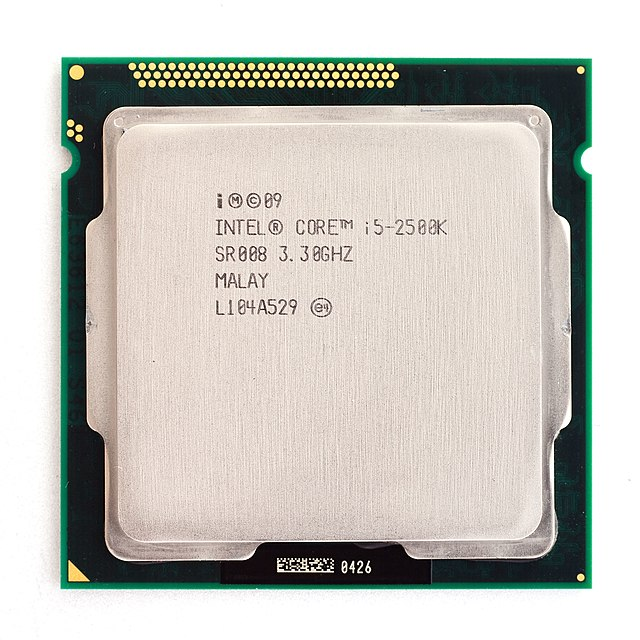
Intel Core i5 Processor
September 2009- Initial Clock Speed: 2.66GHz
- Type: 64-bit, 2 to 4-Core
- Transistors: 774 Million
- Manufacturing Technology: 45 nm

Ashley Pomeroy, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Intel Core i3 Processor
January 7, 2010- Clock Speeds: 2.93 - 3.07GHz
- Type: 64-bit, 2-Cores
- Transistors: 382 Million
- Manufacturing Technology: 32 nm