Table of Content
- Single-Mode Fiber
- Multi-Mode Fiber
- SC Connector (Subscriber Connector)
- ST Connector (Straight Tip Connector)
- LC Connector (Lucent Connector)
- FC Connector (Ferrule Connector/Fiber Channel)
- MT-RJ Connector (Mechanical Transfer Registered Jack)
Single-Mode Fiber
- Single-mode fiber is a type of fiber optic cable through which only one light signal can travel at a time.
- Because single-mode fiber is more resistant to attenuation than multi-mode fiber, it can be used in significantly longer cable runs.
- The core of a single-mode fiber is normally 9 microns wide. A micron is one millionth of a meter.
- Single-mode fiber can support Gigabit Ethernet over distances as long as 10 kilometers.
- The opposite of single-mode fiber is multi-mode fiber.
- Single-mode fiber cables are generally yellow in color,
- Single-mode fiber is sometimes abbreviated as SMF.
Back to Top
Multi-Mode Fiber
- Multi-mode fiber is a type of fiber optic cable which is thick enough for light to follow several paths through the code.
- Multi-mode fiber is best suited for use in short lengths, such as those used in Local Area Networks (LANs) and Storage Area Networks (SANs).
- Multi-mode fiber comes in two standard widths, 62.5 micron and 50 micron. A micron is one millionth of a meter.
- 62.5 micron multi-mode fiber can support Gigabit Ethernet over distances as long as 275 meters; 50 micron multi-mode fiber can increase that range to 550 meters
- The opposite of multi-mode fiber is single-mode fiber.
- Multi-mode fiber is easier to work with than single-mode fiber. The fiber is larger and the tolerances required are much lower.
- Multi-mode fiber is sometimes abbreviated as MMF.
- Multi-mode fiber cables are generally orange in color.
- Multi-mode fiber is generally less expensive than single-mode fiber.
SC Connector (Subscriber Connector)
- The SC connector is a fiber optic connector with a push-pull latching mechanism which provides quick insertion and removal while also ensuring a positive connection.
- The SC connector has been standardized as FOCIS 3 (Fiber Optic Connector Intermateability Standards) in EIA/TIA-604-03.
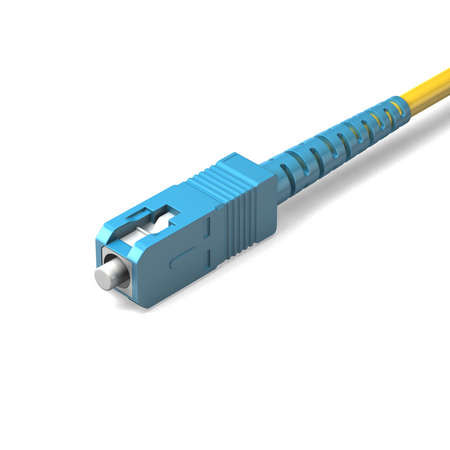
ST Connector (Straight Tip Connector)
- The ST connector is a fiber optic connector which uses a plug and socket which is locked in place with a half-twist bayonet lock.
- The ST connector was the first de facto standard for fiber optic cabling.
- The ST connector has been standardized as FOCIS 2 (Fiber Optic Connector Intermateability Standards) in EIA/TIA-604-02.
- Reference: http://www.thefoa.org/tech/connID.htm

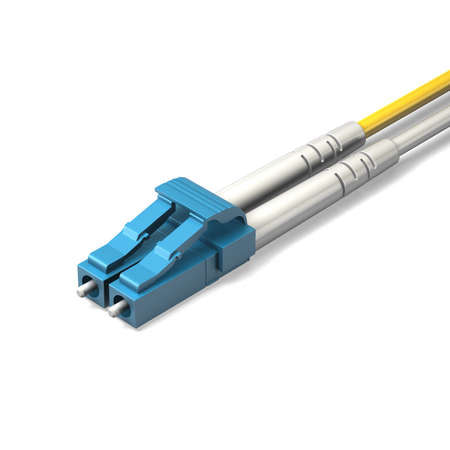
LC Connector (Lucent Connector)
- The LC connector is a small form-factor fiber optic connector.
- The LC connector resembles a small SC connector.
- Lucent Technologies developed the LC connector for use in TelCo environments.
- The LC connector has been standardized as FOCIS 10 (Fiber Optic Connector Intermateability Standards) in EIA/TIA-604-10.
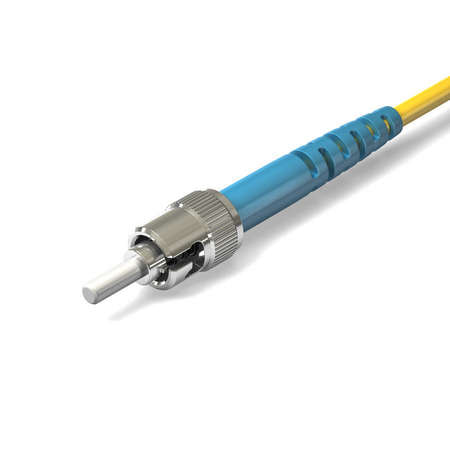
FC Connector (Ferrule Connector/Fiber Channel)
- The FC connector is a fiber optic connector with a threaded body which was designed for use in high-vibration environments.
- The FC connector has been standardized in a FOCIS 4 (Fiber Optic Connector Intermateability Standards) in EIA/TIA-604-04.
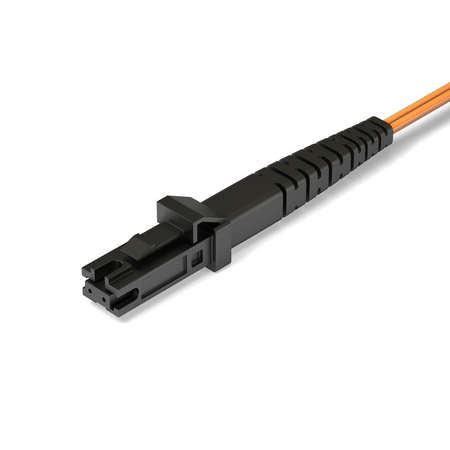
MT-RJ Connector (Mechanical Transfer Registered Jack)
- The MTRJ connector is a small form-factor fiber optic connector which resembles the RJ-45 connector used in Ethernet networks.
- The MTRJ connector was designed by AMP, but was later standardized as FOCIS 12 (Fiber Optic Connector Intermateability Standards) in EIA/TIA-604-12.


